Sensors
Keep getting Information.
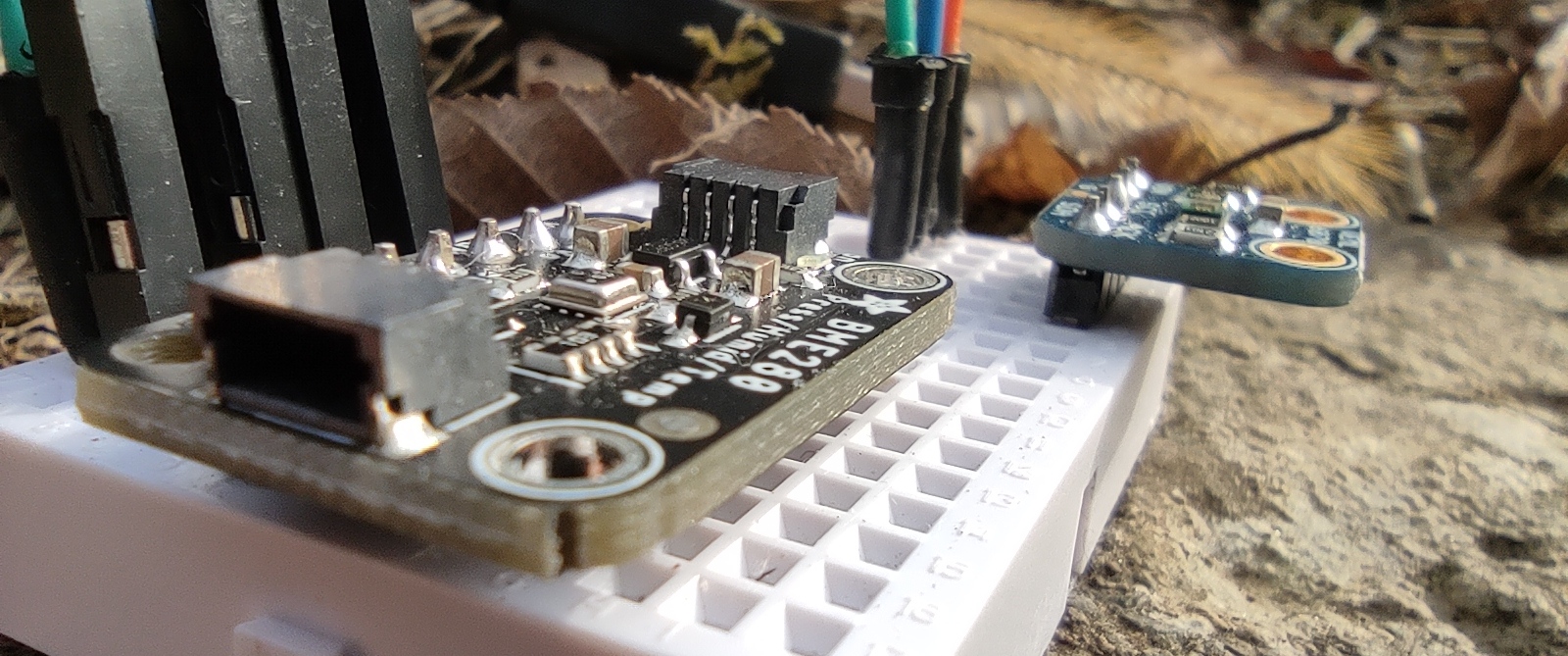

Each IoT application will have different sensors, or even in the case of solutions for agriculture you can have different types of setup depending on the specific application. We will illustrate here the sensors used and the data obtained from them.
Sensors for Agriculture application
As ours is a prototype, we opted for a generic setup that would be useful and suitable for as many applications as possible. The fixed sensor core that we have built consists of:
In addition, in the case of the module designed for outdoors, we have also implemented an:
Collected data
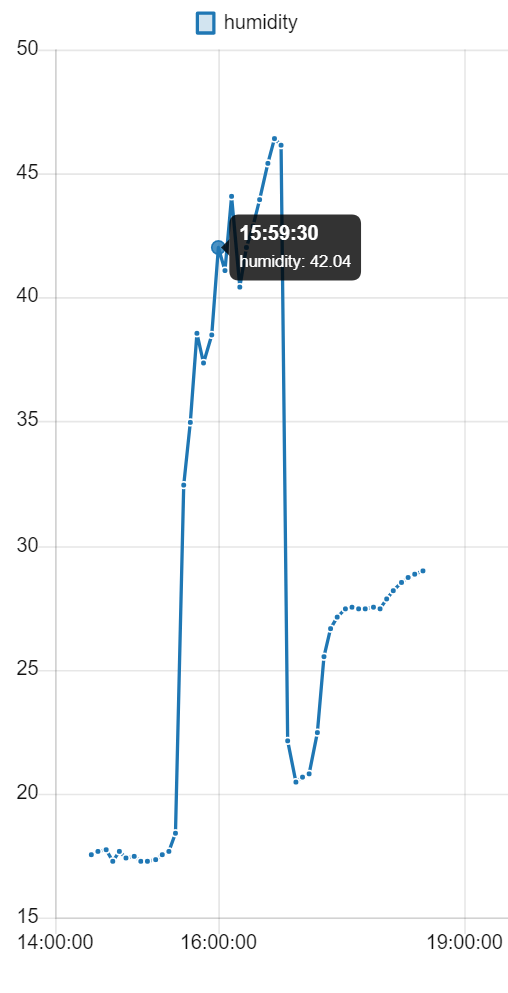
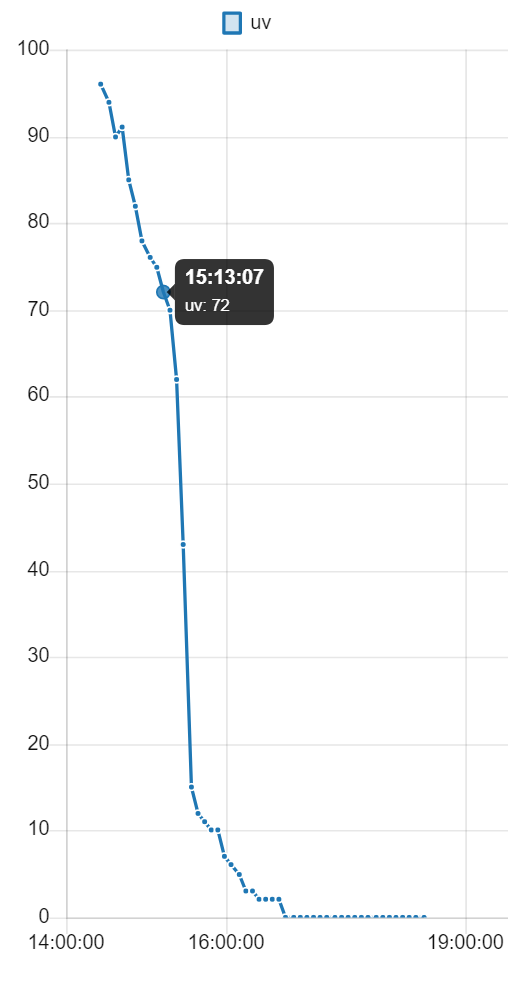
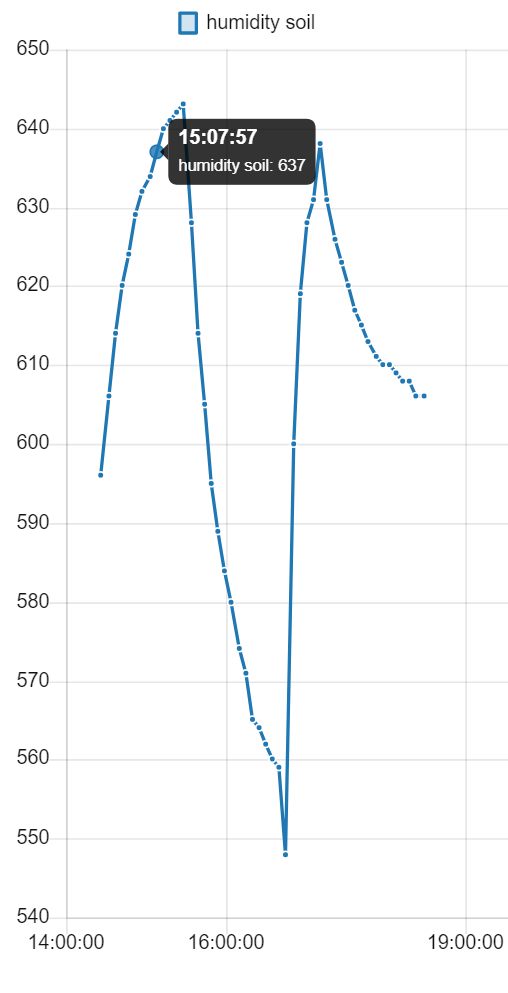
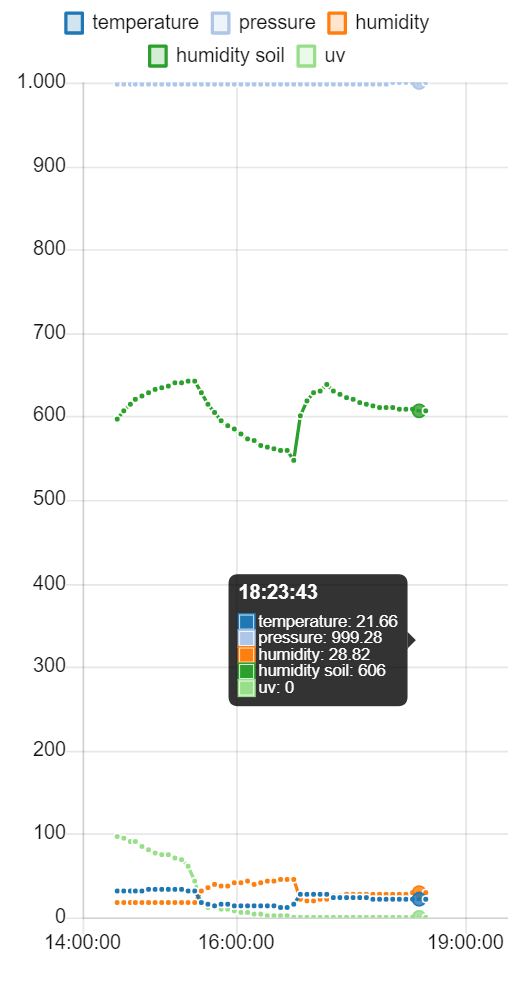
The data collected by the sensors, which are presented in this form:
Data = T:20.29 $ P:995.28 $ H:56.65 $ S:0 $ R:295 $ U:0Are sent by external modules to the gateway and added to a file that can serve as a daily or weekly history of the data obtained, with a graphical interface that creates adaptive graphs to represent them.
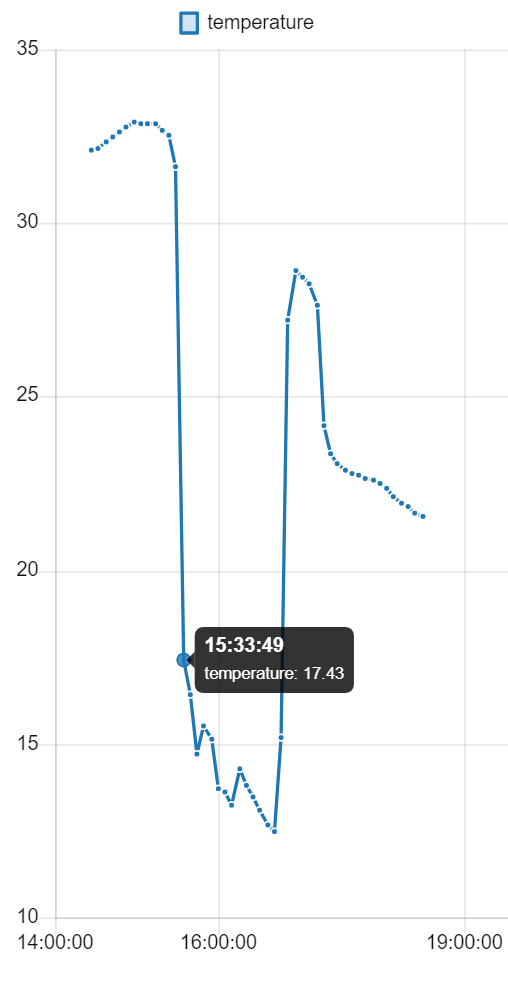
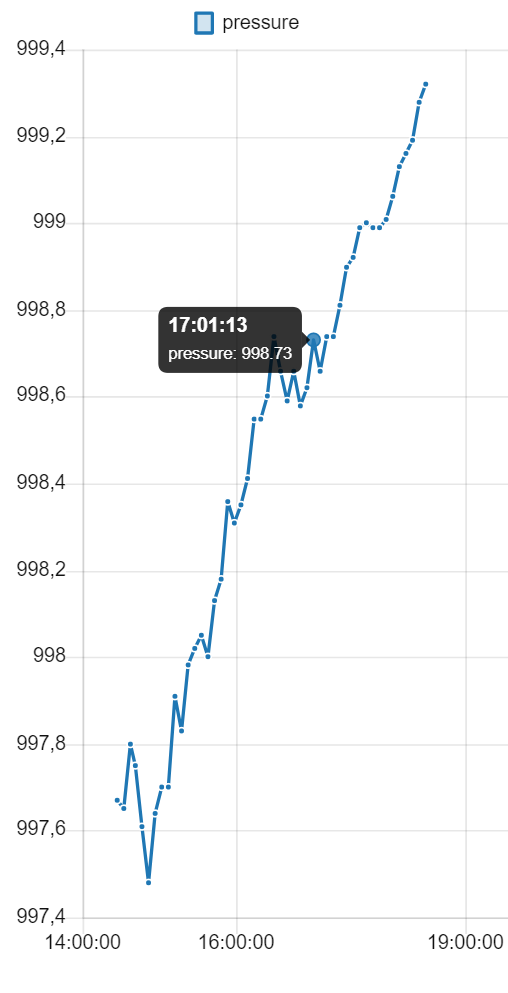
Here are some examples of how the graphs can be displayed: